The Power of Embodiment for Building Empathy
Harnessing the uniquely immersive nature of VR, healthcare professionals can now feel what it’s like to receive care through the eyes of a patient. Flipping training on its head and coming at it from an alternative perspective has opened up learning experiences that foster empathy and deeper understanding.
Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a powerful tool for training, particularly in professions requiring high levels of empathy. One of VR's key advantages is its ability to create immersive simulations that allow learners to experience the world from another person’s perspective. For instance, in healthcare VR the ability of practitioners to ‘step into the shoes’ of their patients enables them to develop greater empathy and consequently provide more personalised and compassionate care.
What is Embodiment in Virtual Reality?
Mel Slater, Professor of Virtual Reality at the University of Barcelona, has highlighted that “most people think of VR as being about being somewhere different, but it can also be about being someone different” (Slater, 2020). Embodiment in VR refers to the sensation of "being" in a virtual body and experiencing the world through its perspective. Unlike traditional methods such as observing consultations or watching videos, VR immerses learners in simulations that can replicate a patient's lived experience. This immersion fosters both sensory and cognitive engagement which can create profound and transformative experiences.
The Neuroscience Behind Virtual Embodiment
The concept of embodiment in VR is grounded in research showing how the brain integrates sensory inputs to construct a sense of self. By synchronising visual and auditory cues, VR enables the brain to accept a virtual body as its own (Kilteni et al., 2012). First-person perspective VR simulations can evoke a strong sense of body ownership, with measurable changes visible on functional MRI.
For example, de Borst et al (2020) found that participants embodying a woman experiencing verbal abuse exhibited synchronised brain activity in regions associated with bodily self-awareness (fronto-parietal network), emotional processing (insular cortex), threat perception (amygdala) and sensory-motor integration (premotor and somatosensory cortices). These findings demonstrate how VR influences emotional responses and bodily self-awareness. Similarly, research by Seinfeld et al (2018) shows that VR activates brain networks related to self-representation and emotional identification, underscoring how embodiment can enhance empathy and deepen understanding of others’ experiences.
Enhancing Empathy in Healthcare
Traditional clinical education often prioritises technical and scientific aspects of care, while the patient's perspective can be often overlooked. Research indicates that medical students trained to understand the patient's viewpoint establish better empathy and communication leading to higher patient satisfaction (Hojat et al., 2002).
Empathy is crucial for effective care as it enables healthcare practitioners to connect with patients in a compassionate, person-centred manner, and embodiment in VR deepens empathy by immersing learners in the physical, emotional and social challenges patients face. This experience also enhances overall emotional intelligence, particularly the ability to recognise, understand and respond to the emotions of others. By stepping into a patient’s shoes, learners better appreciate how their actions and words can influence a patient’s well-being for better or worse.
Leveraging Embodiment for Healthcare Training at Revolve Labs
At Revolve Labs, we harness the power of Virtual Reality to create training modules that equip healthcare staff with the skills and empathy needed to provide excellent patient care. For example, in our module on chronic pain, learners experience the frustration, fatigue and isolation associated with persistent pain, while in our dementia module participants are immersed in scenarios that replicates the confusion, anxiety and emotional distress of cognitive decline. The use of 360-degree 8K video and high-fidelity audio creates a deep sense of immersion, such that learners experience interactions with family members, doctors and nurses, as well as the patient’s own internal thoughts, as if they themselves were the patient.
Summary - embodiment in VR
Harnessing the uniquely immersive nature of VR, healthcare professionals can now feel what it’s like to receive care through the eyes of a patient. Flipping training on its head and coming at it from an alternative perspective has opened up learning experiences that foster empathy and deeper understanding. By incorporating embodiment into VR scenarios at Revolve Labs, we’re delivering training that enhances patient care and supports better healthcare outcomes.
References
de Borst, A.W., Sanchez-Vives, M.V., Slater, M., & de Gelder, B. (2020). First-Person Virtual Embodiment Modulates the Cortical Network that Encodes the Bodily Self and Its Surrounding Space during the Experience of Domestic Violence. eNeuro, 7(3).
Hojat, M., Louis, D. Z., Markham, F. W., Wender, R., & Gonnella, J. S. (2002). Empathy in medical students and its relationship to clinical competence. Journal of Medical Education, 77(6), 429-435.
Kilteni, K., Groten, R., & Slater, M. (2012). The Sense of Embodiment in Virtual Reality. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 1, 9.
Seinfeld, S., Slater, M., Sanchez-Vives, M.V., et al. (2018). Offenders Become the Victim in Virtual Reality: Impact of Changing Perspective in Domestic Violence. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2692.
Slater, M. (2020). Transforming the Self Through Virtual Reality. Front Virtual Reality Online Seminar Series.
Google, Samsung and Apple ‘All In’ on XR
Samsung Project Moohan mixed reality headset (Source: Google)
GooglE and SAMSUNG LAUNCH aNDROID XR and COMPETITOR HEADSET FOR APPLE VISION PRO
The XR industry is abuzz with Samsung and Google’s entry into high-end headsets, joining Apple’s Vision Pro in reshaping immersive technology. Whilst designed as high-end personal consumer devices, these tech giants’ innovations herald significant shifts in the way enterprise training in healthcare sector can be delivered.
Samsung unveiled their XR headset at the recent Snapdragon Summit, set to launch in 2025, whilst the Apple Vision Pro is already demonstrating high-end visual fidelity and seamless user experience. Google’s launch of an Android XR platform will ensure a robust and broad ecosystems.
For a detailed review and hands-on experience, check out the upload VR review
For medical XR, GOOGLE ENTERING THE MARKET IS a pivotal moment. Let’s explore the implications.
The arrival of Samsung, Google, and Apple elevates expectations for high-end consumer XR hardware, alongside the mass-market offering of Meta. the combined approach will be to grow the consumer market further, making devices more common in both consumer and enterprise settings.
This will impact medical training applications by offering a better user experience via:
Sharper visuals, offering improving clarity for detailed anatomical models.
Ergonomic designs and reduced weight tailored for extended sessions, vital for simulations
Powerful processors: Qualcomm’s Snapdragon XR and Apple’s M2 chip enable fluid, real-time rendering.
These innovations bring medical XR tools closer to replicating real-world scenarios, enhancing training realism and subsequent educational impact.
Expanding Access
The tech giants scaling XR will reduce costs, making premium headsets more accessible. This democratisation will empower more universities to incorporate XR into course curricula, smaller hospitals to adopt VR surgical prep tools and the broader use of headset-delivered immersive telemedicine solutions.
Affordable, high-quality hardware could bridge resource gaps, enabling equitable access to advanced medical training tools. The ensuing competition between these players is likely to drive innovation and reduce the unit consumer cost of headsets.
Standardised Software Ecosystems
Unified platforms like Google’s Android and Apple’s ecosystem simplify app development and enhance compatibility, allowing the developers to utilise standard developer kits. Considering the impact this approach had in the smart phone market via the Apple App and Google Play stores, the path to scale in the XR app market seems clear. In the medical XR market, this will mean:
Smarter apps leveraging AI for tailored learning.
Collaborative training environments for multi-user scenarios.
These advancements expand opportunities to create specialised content across medical disciplines. Google lay out their vision here:
Ensuring Standards and Trust - data security is key
Apple’s Vision Pro prioritises safety and usability, as will Samsung and Google. Adopting their standards benefits medical XR by:
Building trust with healthcare regulators.
Streamlining clinical validation processes.
Enhancing device reliability in critical applications.
This alignment accelerates XR adoption in healthcare training.
The entrance of Samsung, Google, and Apple into high-end XR signifies the technology’s maturity. For medical XR, these innovations promise better tools, broader access, and stronger validation frameworks. By embracing these hardware and platform advances, we can revolutionise medical training, equipping professionals with the skills to save lives. Immersive technology is no longer the future — it’s the present.
Revolve Labs create immersive educational experiences using technologies within the XR spectrum described above. The potential for VR in the healthcare sector is limited only by the creativity & ingenuity of those creating and applying the technology.
Contact us to find out more hello@revolvelabs.co.uk
Transforming Conflict Resolution in Healthcare
At Revolve Labs our mission is clear: to revolutionise training through the use of innovative technology. We are excited to be partnering with IKON Training and the XR Labs to bring this vision to life in the realm of conflict resolution, an area vital for healthcare professionals navigating high-stress environments. This project is more than a technical innovation; it represents a new chapter in approaching learning, development and conflict resolution. We are harnessing the power of VR to deploy a programme at national scale to build the resilience needed to navigate today’s complex working environments.
Revolve Labs and IKON Training Unite as project partners
Clinical and non-clinical healthcare professionals (HCPs) face unique challenges balancing patient care with conflict management in emotionally charged situations. IKON Training’s expertise in delivering practical, impactful conflict resolution strategies aligns seamlessly with our specialisation in leveraging virtual reality (VR) for medical education. Together, we’re creating immersive learning experiences tailored to the healthcare sector’s complexities.
We’ve know how VR transforms medical education, enabling learners to practise technical and interpersonal skills in realistic, risk-free environments. For this collaboration, we’ve focused on scenarios healthcare professionals encounter daily, de-escalating tensions with patients, managing workplace conflicts, and maintaining calm during crises. These modules combine cutting-edge VR technology with evidence-based conflict resolution techniques, empowering participants to develop both empathy and practical skills.
Meeting the Needs of Modern Medical Workforce
With patient outcomes often tied to effective communication, our VR-enhanced training modules provide healthcare teams with tools to address conflict constructively. Participants engage in dynamic scenarios that simulate the pressures of real-world healthcare, helping them refine their responses while fostering a culture of collaboration and understanding.
By uniting our technological expertise with IKON Training’s experience, this partnership exemplifies how scenario training can address critical skills gaps for a wide primary care audience, ensuring healthcare professionals are better equipped to handle the human side of medicine. We’re excited about the potential of this collaboration to transform not only conflict resolution but also the broader landscape of healthcare training.
Production techniques
360 video scenarios, green screen expert content and decision tree branching are used to create a personalised user experience within the VR headset. Users feel what it is like to be dealing with an aggressor, giving a greater emotional connection to the learning leading to a memorable and effective learning experience. Users make decisions and receive feedback from IKON Training’s subject matter experts on how to de-escalate.
360 shoot
Personification filming
Subject matter expert from Ikon Training
DEPLOYMENT
At Revolve Labs, we believe this is just the beginning of what VR can achieve in empowering medical professionals. By deploying education modules in managed flight cases, we are able to take in-depth immersive educational experiences to any location.
Want to stay updated?
Follow our journey as we continue to explore the partnership between technology and training. Discover how IKON Training and Revolve Labs are creating transformative learning experiences together. Sign up for our newsletter to learn more about our innovations in medical education and upcoming training opportunities.
How XR is transforming medical training in front of our eyes
It all begins with an idea.
The medical industry is one of the most critical fields where high-quality education and training can directly impact the safety, well-being, and lives of patients. The need for precise, reliable, and practical training methods is at the core of medical education. With the rise of Extended Reality (XR), which includes both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), the landscape of medical training is undergoing a seismic shift. This technology offers new opportunities to address the shortcomings of traditional education methods while providing a more immersive, engaging, and effective way to learn. The fact that this can be delivered at scale through the proliferation of Meta headsets gives a huge opportunity to transform the learning landscape as headsets more accessible to the masses.
In this blog, we explore the core benefits of using XR technology for medical education, with a particular focus on the power of 360-degree immersion, repeatability of complex procedures or diagnostic decisions, emotional engagement, and the growing body of evidence supporting the efficacy of these innovations.
The Educational Promise of full 360-Degree Immersion
One of the most significant advantages of XR in medical training is the ability to create fully immersive, 360-degree environments. With VR, medical students and professionals can enter simulations that recreate realistic hospital settings, operating rooms, and even complex surgical procedures. Unlike traditional textbooks or 2D videos, VR allows users to engage with their surroundings in a fully interactive 3D space.
This level of immersion is vital for understanding anatomy, surgical techniques, and medical procedures that are difficult or impossible to replicate in real life without risk. For example, learners can virtually step into a patient’s body to study internal organs, or observe a surgery from multiple angles in a way that would be impractical in a real-world scenario. Multiple studies have shown that VR’s immersive capabilities can significantly improve knowledge retention and spatial awareness, which are critical for tasks such as surgery or diagnosing rare conditions.
VR’s immersion offers the potential for replicating various scenarios that a medical professional might face. Within primary care, rare condition simulations allow for valuable exposure to situations that would otherwise be unavailable to simulate. Another valuable approach is simulating common conditions in order to optimise the patient pathway through complex healthcare systems.
Repeatability and Mastery of Skills
A core benefit of XR in medical education is the ability to repeat complex procedures as many times as needed. In traditional settings, learners may only have one chance to observe or practice a procedure, particularly in a busy hospital environment. However, with XR, users can practice medical procedures or even entire surgeries repeatedly, without the constraints of real-world scheduling or resource limitations. This ability to practice over and over increases the opportunity for mastery and muscle memory development, which is essential in surgical settings.
For example, a surgical trainee can practice delicate procedures—such as suturing or laparoscopic techniques—without the fear of making a mistake that could harm a patient. They can experiment with different methods, refine their skills, and receive instant feedback on their performance. Studies have shown that learners who use VR for repetitive training experience increased skill acquisition and retention. The act of performing a procedure multiple times helps consolidate learning, reinforcing correct techniques and minimising errors.
Additionally, VR allows users to simulate complex procedures that require precision and speed, offering them the chance to improve both. Because there’s no fear of harming a patient or damaging valuable resources, trainees can engage in trial and error, learning from their mistakes and reinforcing their successes. This repeated exposure also strengthens critical thinking and decision-making skills, which are essential for medical professionals dealing with unexpected challenges in real-world scenarios.
Emotional Engagement and Connection to Learning
Medical training is often viewed as a purely technical skill-building process. However, emotional engagement plays a crucial role in learning, especially in fields like medicine, where empathy and human connection are essential. VR, with its highly immersive nature, is uniquely positioned to create an emotional connection between learners and the content they’re studying. This emotional connection can enhance the retention of knowledge, improve decision-making, and foster better patient care.
For instance, VR can simulate interactions with patients, providing learners with an opportunity to practice communication skills in realistic scenarios. Whether it's breaking difficult news to a patient, managing a patient’s emotions, or delivering care in an empathetic manner, VR allows medical professionals to navigate these sensitive interactions in a controlled, low-stakes environment. These scenarios are vital because they help develop the interpersonal skills that are just as critical as technical skills in medicine.
Furthermore, emotional engagement in VR scenarios can enhance understanding and retention by creating more memorable learning experiences. Research in education has shown that emotional involvement in learning can lead to improved outcomes, as learners are more likely to remember and apply knowledge when it is associated with emotional experiences. By immersing trainees in lifelike scenarios, VR enables learners to connect with the material on a deeper level, fostering long-term retention.
Teamwork and Human Factors
Immersive VR can be a powerful tool for training surgical teams in the field of human factors, which focuses on improving teamwork, communication, decision-making, and other non-technical skills crucial for patient safety. By simulating high-pressure environments where human error could lead to serious consequences, VR allows teams to practice managing stress, coordinating effectively, and improving interpersonal communication without real-world risks. This type of training can enhance situational awareness and collaboration, fostering a more cohesive, efficient team capable of handling complex surgical procedures under pressure.
Evidence of Efficacy in Medical XR Training
The effectiveness of XR technology in medical education is not just theoretical—there is a growing body of evidence supporting its efficacy. Studies have demonstrated that VR and AR can significantly improve learning outcomes in medical education by increasing engagement, enhancing knowledge retention, and improving practical skills.
Source: https://www.pwc.co.uk/issues/technology/immersive-technologies/study-into-vr-training-effectiveness.html
Further evidence from a study conducted by the University of Michigan Medical School found that VR-based training improved the ability of medical students to understand human anatomy. The immersive 3D models allowed learners to engage with the material interactively, providing a deeper understanding of the body’s structures and how they relate to medical procedures. The study concluded that VR could enhance medical education by offering students an experience that was more engaging and effective than traditional methods.
The Future of Medical Education with XR
XR technology will undoubtedly play an even larger role in shaping the future of medical education. The ability to train healthcare professionals more effectively, in more specialized areas, at a fraction of the cost and risk of traditional training methods, is a game-changer for the healthcare industry.
Moreover, the accessibility of VR and AR training tools means that students from around the world can benefit from high-quality, scalable education. In developing countries or regions where access to high-end medical institutions is limited, XR can provide training opportunities that would otherwise be unavailable. This democratisation of medical education ensures that more healthcare workers are well-prepared to deliver safe and effective care.
The integration of XR technology in medical education is a groundbreaking development that has the potential to revolutioniase how medical professionals are trained. From 360-degree immersion to the ability to repeat procedures as many times as necessary, VR and AR offer unprecedented opportunities for learning, mastery, and emotional connection to the material.
As the technology matures, the potential for XR in medical education is vast—offering better outcomes, improved safety, and ultimately, a more prepared and effective healthcare workforce. As a startup company in the XR space, we push the boundaries of how VR approaches improve learning and skill acquisition in a range of medical settings.
Demystifying XR
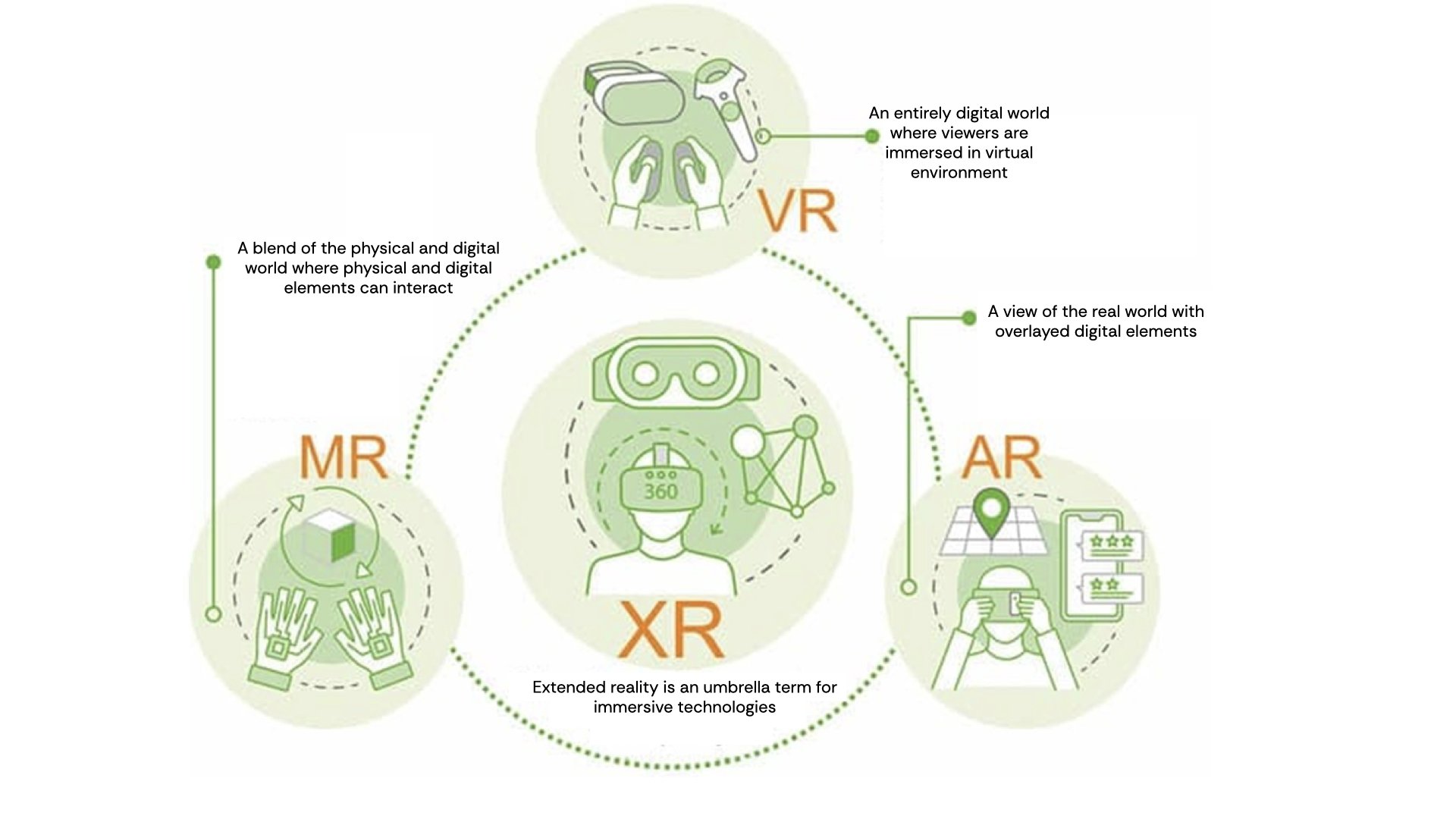
Why are there so many abbreviations in the XR field and what do they actually mean?
For those new to the immersive technologies the abbreviations of VR, AR, MR and XR can be confusing. A wide range of technologies fall within the Extended Reality (XR) spectrum, accessible on a range of hardware devices including VR headsets, smart glasses and smart phones.
Extended Reality, or XR, is an overarching term for immersive technologies, including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). The technologies combine or mirror the physical world with a "digital twin world" able to interact with it, giving users an immersive experience by being in a virtual or augmented environment. Another way to consider the XR spectrum is as a circular diagram of complimentary technologies:
Virtual Reality (VR):
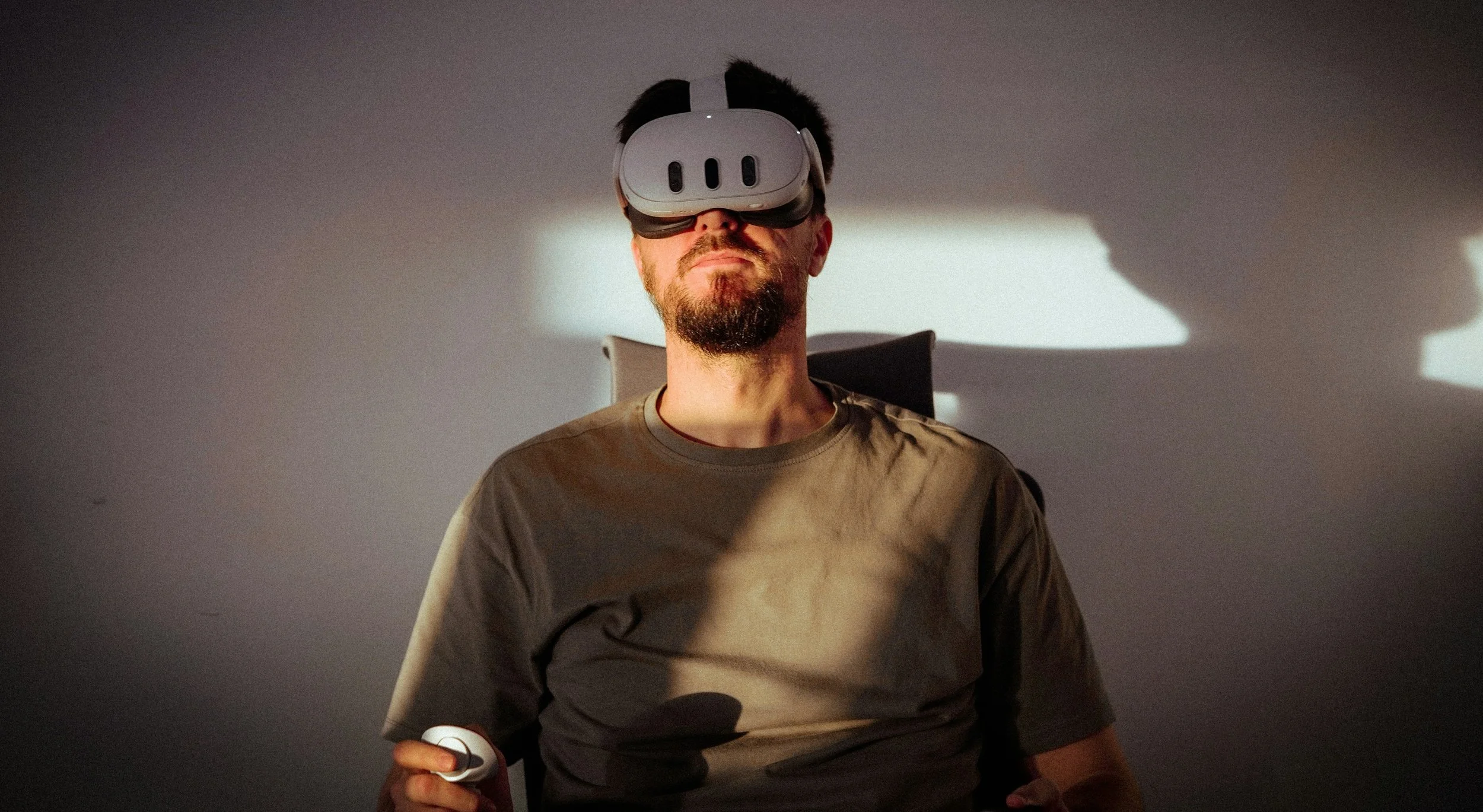
Puts users inside a virtual environment. VR users typically wear a headset that transport them into an entirely virtual world — one moment they’re standing in a real room, and the next they’re immersed in a simulated digital environment. VR immerses users in a fully, making it a powerful tool for medical training and therapy. By wearing a VR headset, training can be delivered in a simulated clinical space with virtual equipment and patients. This gives users an experience without the costs of accessing medical facilities, and without any risks to real patients. The image below shows a surgeon using VR to train for a knee replacement procedure.
Credit: Ghpst
Augmented Reality (AR):
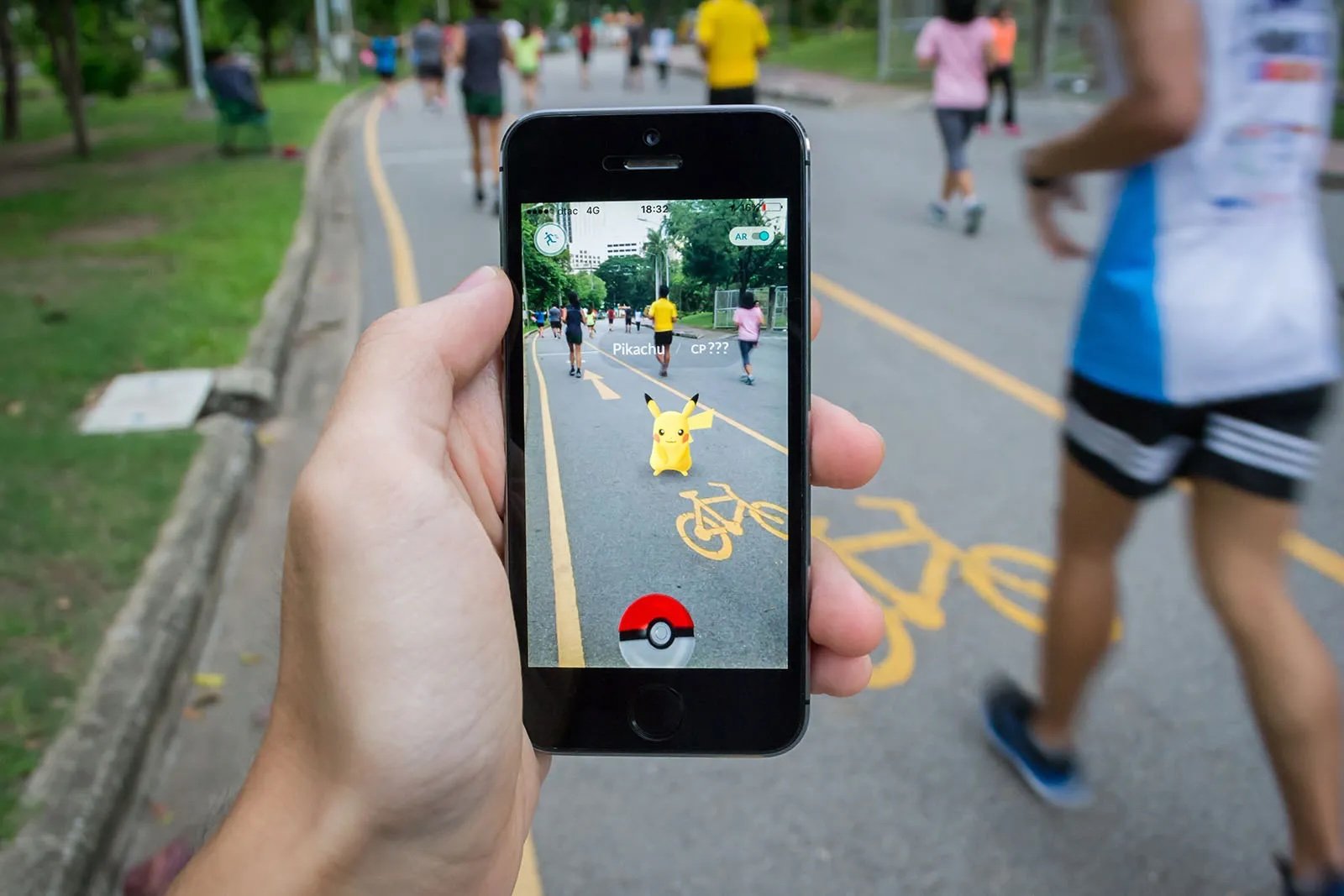
AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, The mobile game Pokémon GO famously brought AR to the mainstream by showing computer-rendered monsters on smartphone screens that players could collect by walking their around their neighbourhoods.
Within medicine, AR can provide doctors with critical, real-time visual information. Within surgery It can be used to project a patient’s anatomy onto their body, guiding surgeons with unprecedented precision. The advantage of AR is that the user can maintain real-world situational awareness, whilst having a digital image incorporated with their view of the world. AR also supports medical education giving trainees a detailed view of 3D models of anatomy through tablets or smartphones, making learning more interactive and accessible.
PokemonGo
Credit: Microsoft
Mixed Reality (MR):
MR blends physical and digital elements, enabling direct interaction between them. In healthcare, MR is being used to enhance telemedicine, allowing doctors to examine virtual representations of a patient’s body while communicating remotely.
Additionally, MR headsets are enabling collaborative tele-surgery and collaborative pre-operative planning. Surgeons can manipulate 3D holograms of a patient’s anatomy segmented into systems to plan and minimise hazards in complex procedures. Colleagues and trainees can ‘dial in’ to witness the procedure or collaborate in real time via the headset device.
In orthopaedic procedures, MR allows for a hybrid view where the surgeon interacts with both the real patient and a holographic overlay, ensuring precise alignment of prosthetic components.
Source: Augmedics
Source: St Josephs Healthcare London
Revolve Labs create immersive educational experiences using technologies within the XR spectrum described above. The potential for VR in the healthcare sector is limited only by the creativity & ingenuity of those creating and applying the technology. Extended reality tools are radically change the way learning is designed and delivered.
If you’d like to discuss how we can bring your Virtual Reality project to life get in touch: hello@revolvelabs.co.uk
Watch our Showreel of recent XR projects